The Riemann Zeta function is a function of a complex variable that analytically continues the sum of the Dirichlet series
In 1737, the revered Swiss mathematician, Leonhard Euler, discovered the fundamental connection between the Zeta function and prime numbers. The proof is as follows, given
we will multiply both sides of the equation by
then subtract from
to remove all factors of 2
Repeating this for factors of 3
and so on. If we continue this process to infinity for , where
is a prime, the expression reduces to
which can be rearranged to produce
So why are we doing all of this? Well, it turns out the reciprocal of the Zeta function has some remarkable properties of its own.
Consider the inverse based on Euler’s prime product formula
expanding this expression we have
which can be rearranged to demonstrate
On close examination one can see that the numerator in actually corresponds to the values of the Möbius function
. Indeed, the reciprocal of the Zeta function can be formally defined by
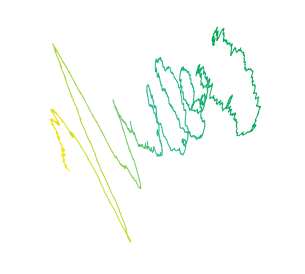
This means that we can indeed deploy Riemann’s Zeta function to model a random walk.